Found 1 results
Article
11 April 2024Exploring Bi4V2O11 as Photoanode for Water Splitting with a Wide Range of Solar Light Capture and Suitable Band Potential
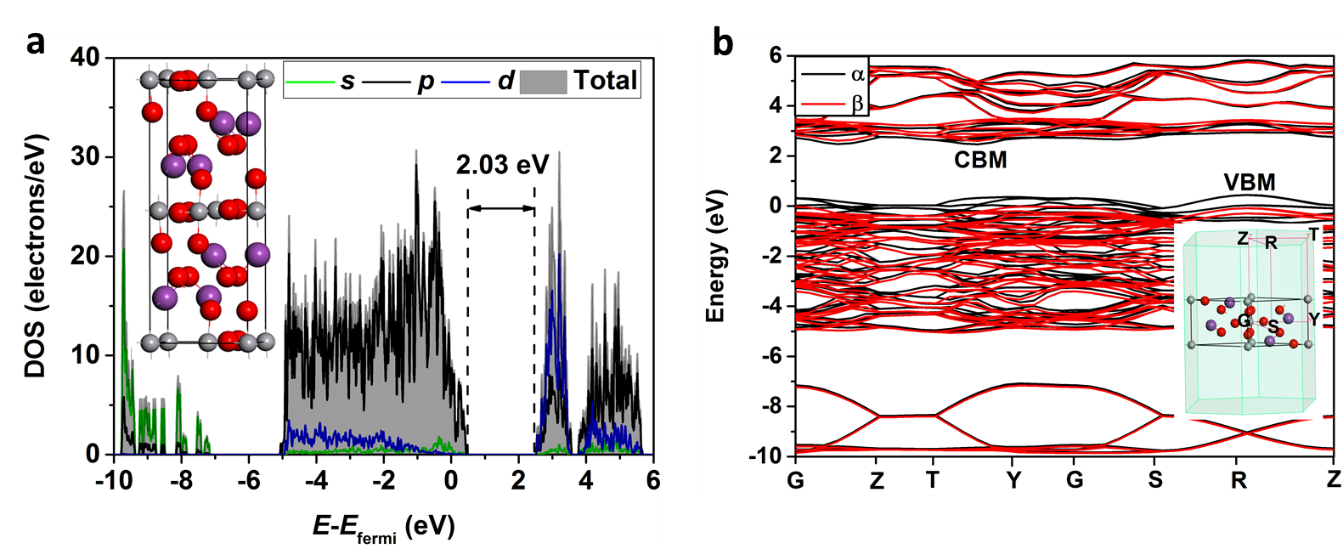
Bi4V2O11 possesses a bandgap of ~1.9 eV, and the band positions of minimum conduction band and maximum valence band straddle the redox potentials of H+/H2 and O2/H2O. In the current work, photoanode made of particulate Bi4V2O11 film displays a wide range of light adsorption. However, when the anode was fabricated by drop-casting and examined for photoelectrochemical water splitting, the photocurrent density of the pristine Bi4V2O11 was low. Improvement has then been carried out by Mo-doping. The Mo-doped Bi4V2O11 photoanode achieves a maximum photocurrent density of 0.3 mA/cm2 after a post deposition necking treatment to improve the connectivity of the drop-cast particles in the film. This material also shows a stability with maintaining 80% photocurrent after 2 h test. Discussion has been made on the displayed performance in PEC water splitting of the Bi4V2O11 materials. Potential solutions have been proposed for this type of promising photoanode material for water splitting.